Tomentella atrobadia H.S. Yuan & Y.C. Dai 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF555627; Facesoffungi number: FoF 05602
Holotype: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Xifeng County, Binglashan National Forest Park, on rotten angiosperm branch, 2 August 2016, Yuan 11099 (IFP 019243, holotype); on rotten angiosperm wood debris, 2 August 2016, Yuan 11114 (IFP 019244).
Morphological description
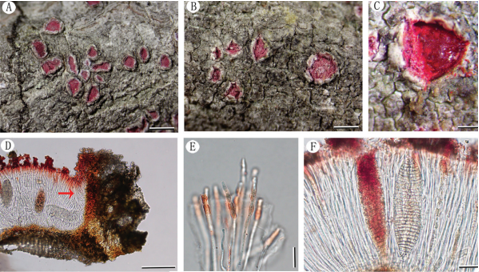
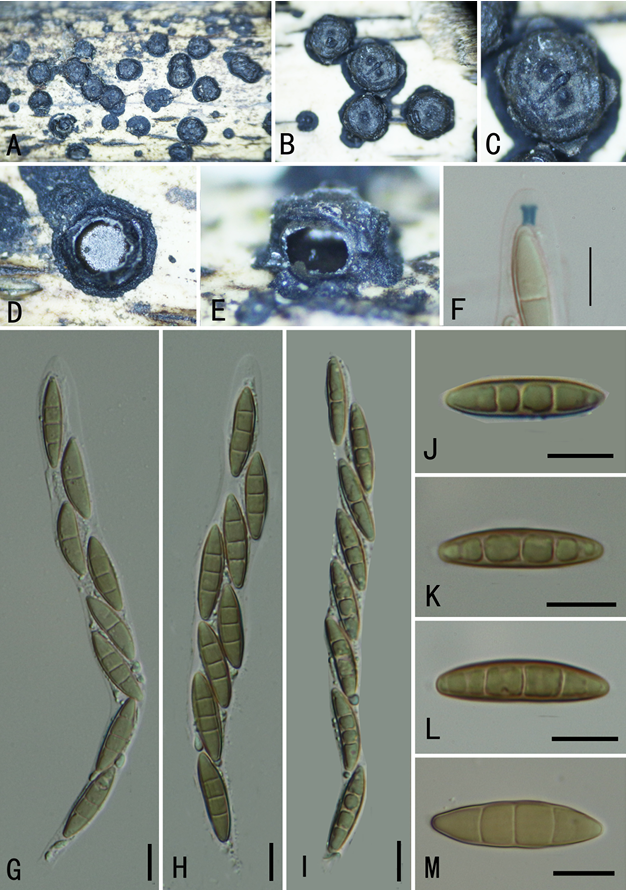
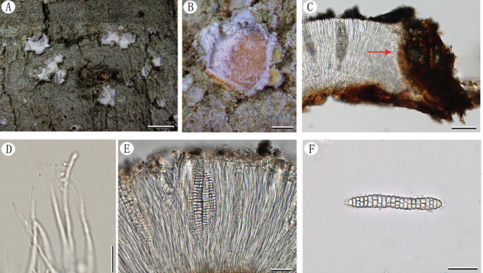
Basidiocarps annual, resupinate, adherent to the substrate, crustose, without odour or taste when fresh, 0.5–0.8 mm thick, continuous. Hymenophoral surface smooth, dark brown (6F5–7F5) and paler than subiculum when dry. Sterile margin often indeterminate, byssoid, concolorous with (n=60/2), globose, subglobose, triangular or lobed in frontal view and subglobose to ellipsoid in lateral view, echinulate to aculeolate, yellow in KOH, yellow in distilled water, cyanophilous, inamyloid; echinuli usually isolated, sometimes grouped in 2 or more, up to 1.5 μm long.
Habitat: On rotten angiosperm branch.
Distribution: In China.
GenBank Accession: ITS: KY686248, KY686249; LSU: MK446335, MK446336.
Notes: Tomentella stuposa (Link) Stalpers is similar to T. atrobadia by having continuous and brown-coloured basidiocarps adherent to the substrate, a smooth hymenophoral surface, thick-walled hyphae, globose basidiospores of approximately the same size and the absence of rhizomorphs. However, T. stuposa is diferentiated by having simple septate subicular hyphae, thin-walled subhymenial hyphae and triangular or lobed basidiospores (Kõljalg 1996). T. alpina Peintner & Dämmrich is similar to T. atrobadia by having continuous basidiocarps adherent to the substrate, smooth hymenophore, the absence of rhizomorphs, clamped and thick-walled subicular hyphae and globose or subglobose basidiospores. But, the former species has distinctly smaller basidospores (6.5–8.5 μm diam, Peintner and Dämmrich 2012).
Reference: Hai‑Sheng Yuan1,2· Xu Lu1,2 · Yu‑Cheng Dai3 ·
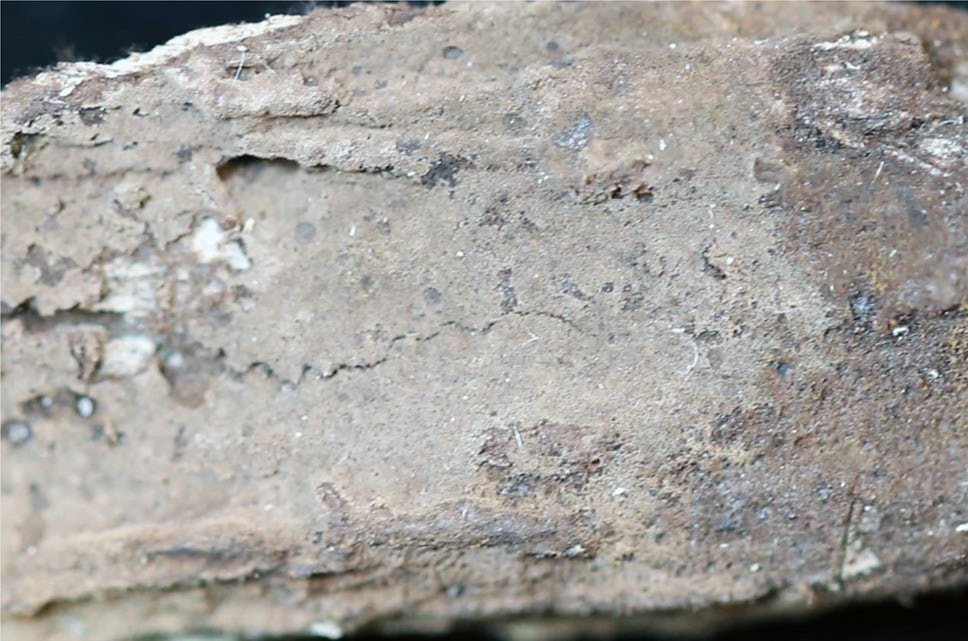

A basidiocarp of Tomentella atrobadia (IFP 019243, holotype)