Gymnosporangium annulatum Y.M. Liang & B. Cao, sp. nov. 2020
MycoBank MB824628
Holotype: CHINA. GANSU: Gannan, Zhuoni (34°25′09″N, 103°34′50″E; 2658 m above sea level [asl]), on Cotoneaster sp., 17 Aug 2014, B. Cao, C.M. Tian, & Y.M. Liang CB120 (holotype BJFC-R01456).
Morphological description
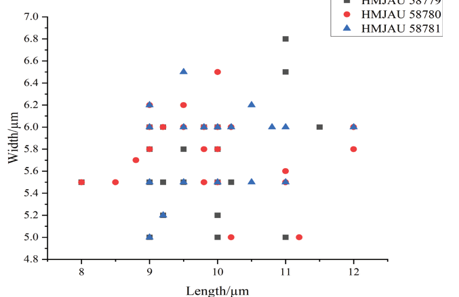
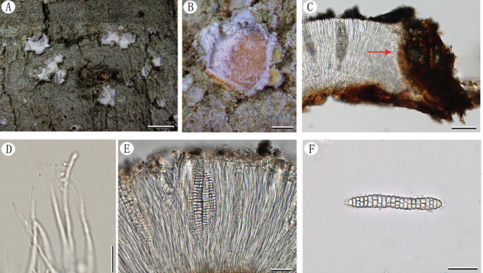
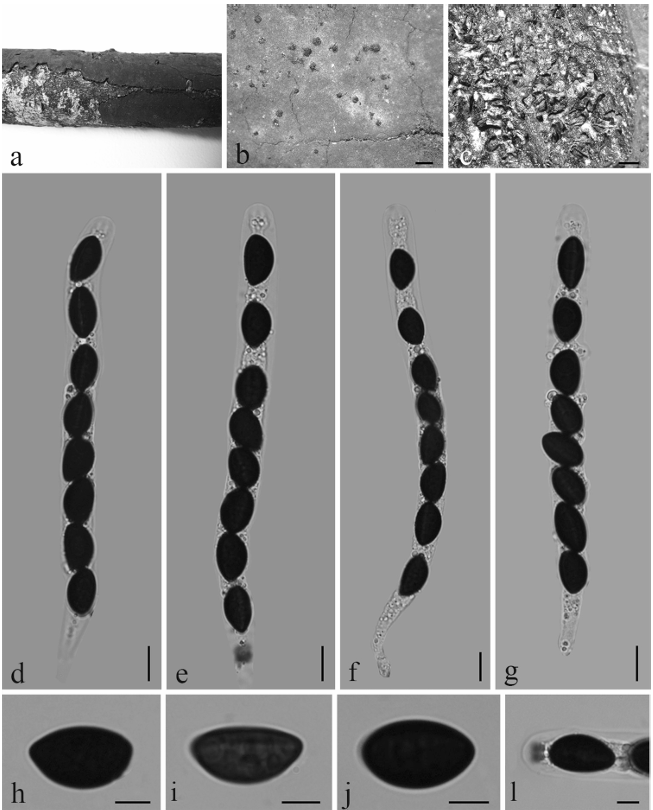
Spermogonia epiphyllous or fructicolous, aggregated in groups, pale yellow to black. Aecia hypophyllous or fructicolous, roestelioid, 1–2 mm long, peridium becoming dehiscent at apex, peridial cells rhomboid, 42–112 × 14–30 μm, inner wall and side wall rugose (type R), outer wall smooth (type S). Aeciospores globoid or ellipsoid, yellowish brown, 21–28 × 17–26 μm, wall 1–2.5 μm, large annulate (type LA), more than 5 pores, scattered. Uredinia and telia not found.
Habitat: on Cotoneaster sp
Distribution: Gansu and Qinghai in China
GenBank Accession: ITS2 MH178662; 28S MH184510; tef1 MH202934
Notes: The aeciospore surface structure of G. annulatum is large annulate (type LA). Gymnosporangium distortum and G. echinulatum also have this kind of structure; however, G. distorum can cause malformation of the hosts, and the aeciospores are somewhat larger (25–35 × 19–25 μm) than those of G. annulatum. The inner wall of peridial cells of G. echinulatum is sparsely echinulate (type SE), which can be used for species discrimination. All three species can be separated based on phylogenetic results.
Reference: Si-Qi Tao, Bin Cao, Makoto Kakishima et al. (2020) Species diversity, taxonomy, and phylogeny of Gymnosporangium in China.
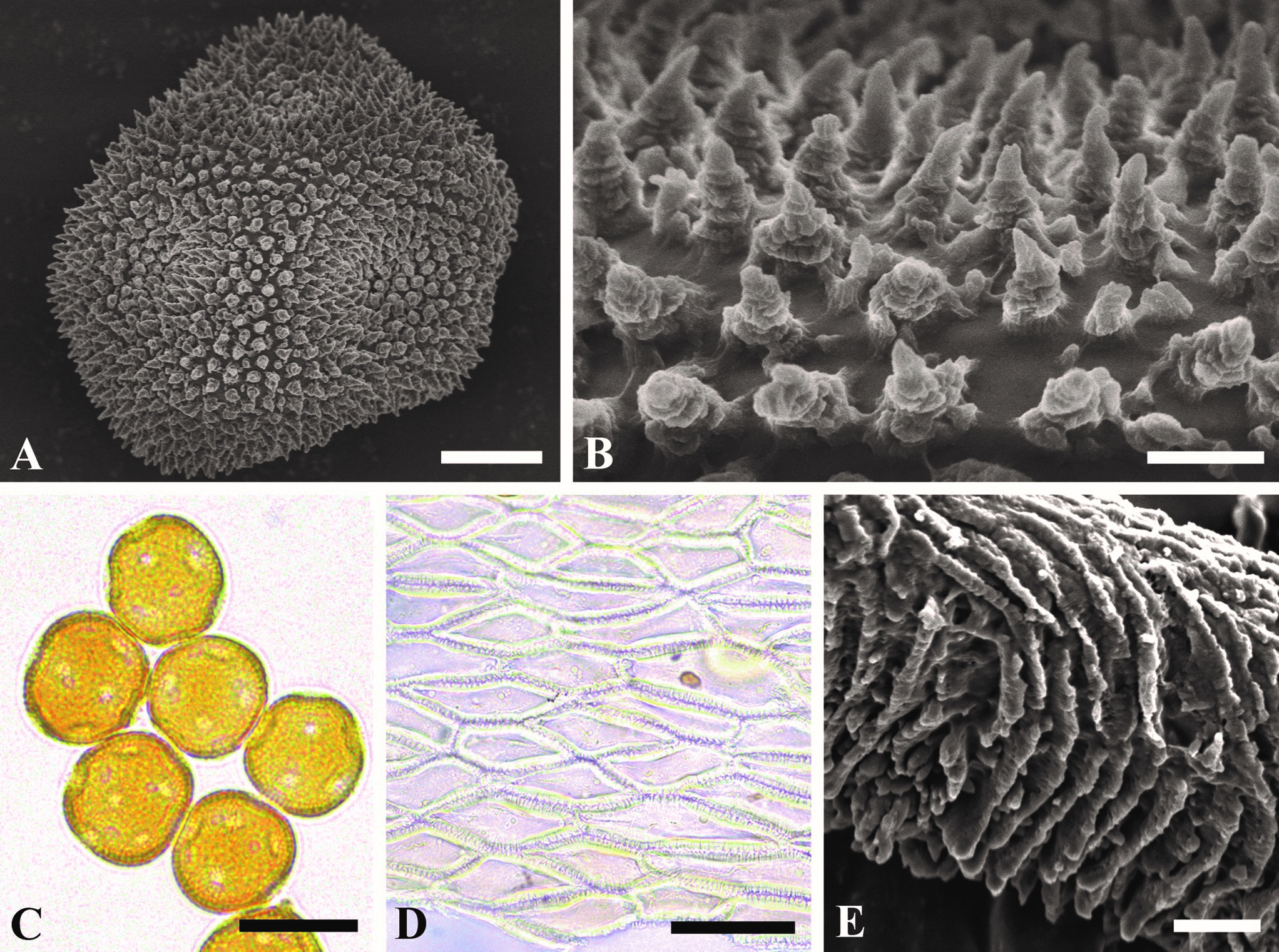
Aecial stages of Gymnosporangium annulatum. A, B. Surface structure of aeciospores. C. Aeciospores. D. Peridial cells. E. Surface structure of peridial cells. Bars: A = 5 μm; B = 1 μm; C = 20 μm; D = 70 μm; E = 2 μm.