Gymnosporangium pleoporum Y.M. Liang & B. Cao, sp. nov. 2020
MycoBank MB824627
Holotype: CHINA. QINGHAI: Menyuan (37°09′ 48″N, 102°01′40″E, 2886 m asl), on Juniperus przewalskii, 4 May 2017, Bin Cao C229 (holotype BJFC-R02952).
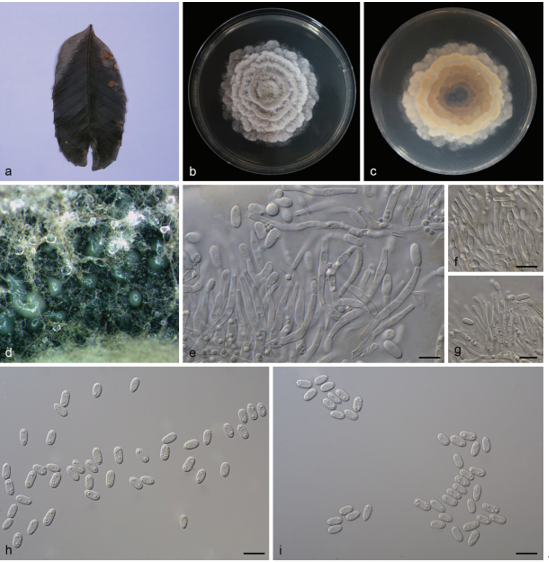
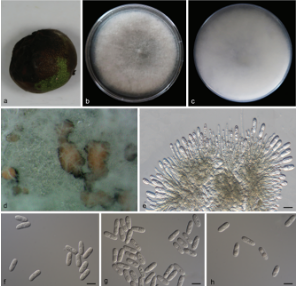
Morphological description
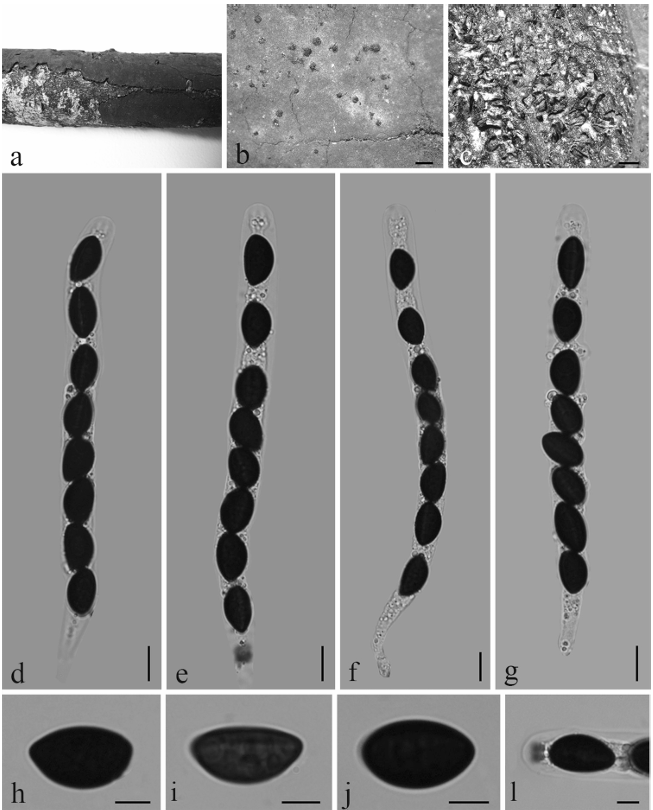
Spermogonia, aecia, and uredinia not found. Telia foliicolous, not causing hypertrophy, pulvinate, 1–2 mm high, black brown. Teliospores 2-celled, rarely 1-celled, 54–84 × 20–27 μm, wall 1–3 μm thick, brown to dark brown, fusiform, apex conical, constricted at the septum, pores 5–8 in each cell, scattered, pedicel cylindrical, hyaline.
Habitat: on Juniperus przewalskii
Distribution: Qinghai in China.
GenBank Accession: ITS2 MH178658; 28S MH184506; tef1 MH202930.
Notes: Most Gymnosporangium teliospores have 2 pores in each cell (Kern 1973). This species was identified as a novel species for it has several pores (5–8) with a scattered arrangement. Four other Gymnosporangium species reported with more than 2 pores per cell: G. atlanticum, G. gjaerumii, G. multiporum, and G. taianum. However, G. pleoporum differs from G. atlanticum and G. taianum mainly in the scattered arrangement of pores, and the latter two species having several pores in a transverse zone (Kern 1973; Zhuang et al. 2012; Fernández et al. 2016). Gymnosporangium gjaerumii teliospores have 4 pores located more or less close to the septum (Azbukina 1997), whereas G. pleoporum has more pores (5–8) in each cell. Finally, G. multiporum resembles G. pleoporum in the number and distribution of the pores, but it has 8) with a scattered arrangement. Four other Gymnosporangium species reported with more than 2 pores per cell: G. atlanticum, G. gjaerumii, G. multiporum, and G. taianum. However, G. pleoporum differs from G. atlanticum and G. taianum mainly in the scattered arrangement of pores, and the latter two species having several pores in a transverse zone (Kern 1973; Zhuang et al. 2012; Fernández et al. 2016). Gymnosporangium gjaerumii teliospores have 4 pores located more or less close to the septum (Azbukina 1997), whereas G. pleoporum has more pores (5–8) in each cell. Finally, G. multiporum resembles G. pleoporum in the number and distribution of the pores, but it has shorter teliospores (45–51 × 20–24 μm) compared with G. pleoporum (54–84 × 20–27 μm) (Kern 1973). In previous studies, only G. huanglongense and G. przewalskii were reported on J. przewalskii (Cao et al. 2016, 2017). In this research, the new taxon was collected from the same host. However, it can be distinguished from G. huanglongense and G. przewalskii by its teliospores possessing 5–8 scattered pores in each cell, the phylogenetic analysis shows that the new species is distinct.
Reference: Wang Z, Liu Y, Wang HM et al. (2020) Ophiostomatoid fungi associated with Ips subelongatus, including eight new species from northeastern China
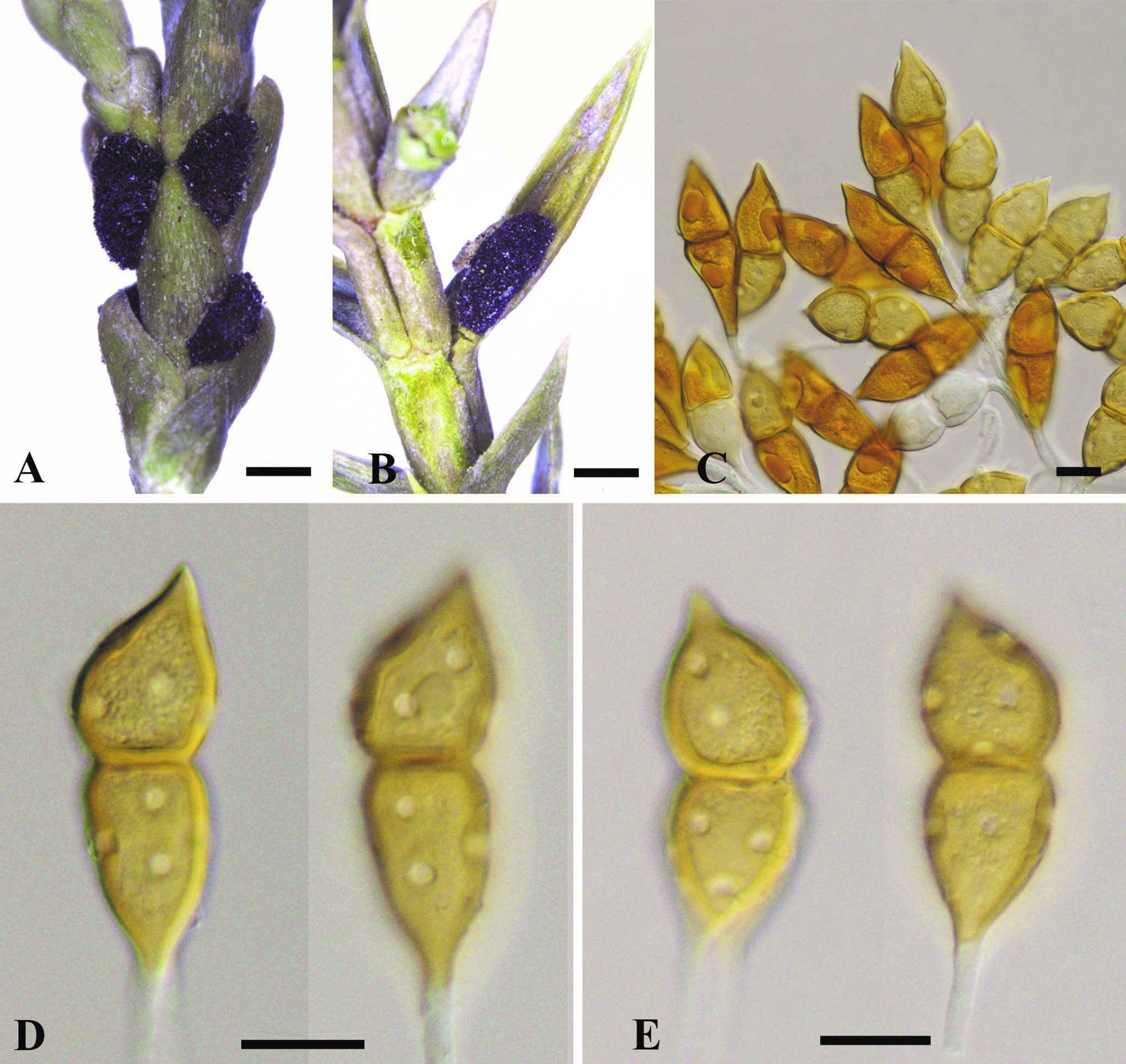

elial stages of Gymnosporangium pleoporum. A, B. Telia. C–E. Teliospores. Bars: A, B = 1 mm; C–E = 20 μm.